Emergency Vs Planned hospitalization cashless claim process
The cashless claim process in health insurance can differ between emergency and planned hospitalizations. Here’s an overview of the distinctions between these two scenarios:
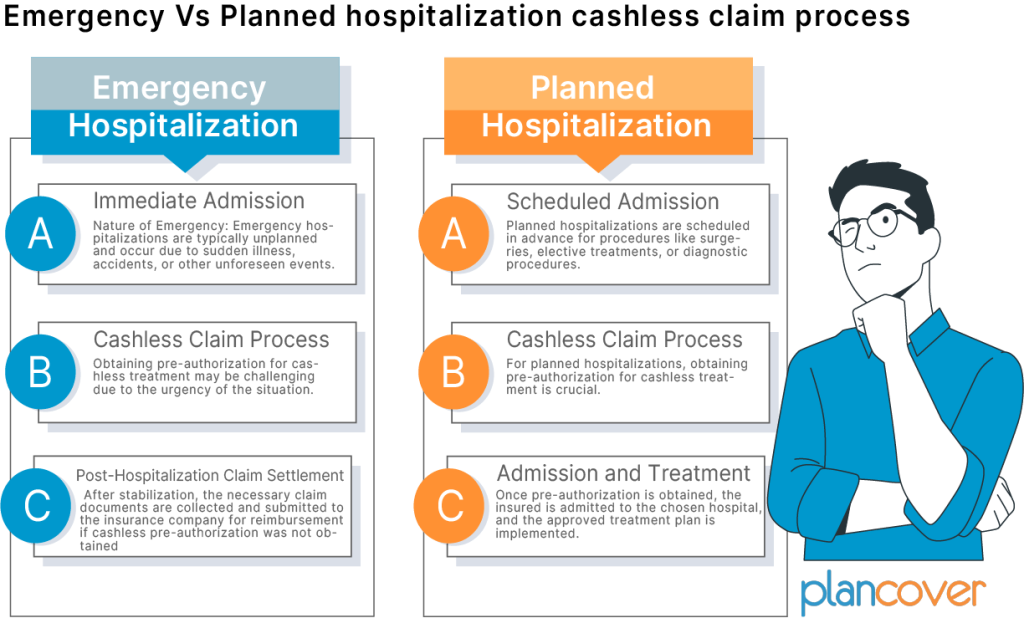
Emergency Hospitalization:
Immediate Admission:
Nature of Emergency: Emergency hospitalizations are typically unplanned and occur due to sudden illness, accidents, or other unforeseen events.
Immediate Care: In emergency situations, the priority is to provide immediate medical care. The insured individual may be taken to the nearest hospital that can address the emergency.
Cashless Claim Process:
Pre-authorization Challenges: Obtaining pre-authorization for cashless treatment may be challenging due to the urgency of the situation. However, many insurance companies have provisions for post-authorization in emergencies.
Informing the Insurer: The insured or their family needs to inform the insurance company as soon as possible after hospitalization, providing details of the emergency.
Post-Hospitalization Claim Settlement:
Claim Documentation: After stabilization, the necessary claim documents are collected and submitted to the insurance company for reimbursement if cashless pre-authorization is not obtained.
Retroactive Authorization: In some cases, the insurance company may retroactively authorize cashless treatment, provided the emergency was genuine and the treatment was covered.
Planned Hospitalization:
Scheduled Admission:
Nature of Planned Hospitalization: Planned hospitalizations are scheduled in advance for procedures like surgeries, elective treatments, or diagnostic procedures.
Choice of Hospital: The insured has the opportunity to choose a network hospital for planned hospitalization, optimizing benefits.
Cashless Claim Process:
Pre-Authorization: For planned hospitalizations, obtaining pre-authorization for cashless treatment is crucial. The insured or the hospital initiates this process by submitting relevant documents to the insurance company.
Verification and Approval: The insurance company reviews the pre-authorization request, verifies policy coverage, and approves the treatment plan if it meets the policy terms.
Admission and Treatment:
Hospital Admission: Once pre-authorization is obtained, the insured is admitted to the chosen hospital, and the approved treatment plan is implemented.
Direct Settlement: The hospital bills are directly settled by the insurance company as per the pre-approved amount.
Post-Hospitalization:
Documentation: The insured may need to submit additional documents post-hospitalization, such as original bills, medical reports, and discharge summaries.
Reimbursement (if required): If there are any non-network expenses or if the insured opts for a hospital outside the network, reimbursement is processed based on the submitted documents.
In summary, while both emergency and planned hospitalizations may involve cashless claims, the process can vary based on the nature of the situation. Emergency hospitalizations focus on immediate care, and cashless approval may be obtained post-hospitalization. In contrast, planned hospitalizations require pre-authorization to ensure a smooth and direct settlement process. Insured individuals should be aware of the specific procedures outlined in their health insurance policy and communicate with the insurance company accordingly.