Maternity Insurance Waiting Periods: Your Guide to Planning Ahead
When planning a family in India, understanding the financial implications of pregnancy and childbirth is crucial. Maternity insurance offers a safety net, but the waiting period—a timeframe after purchasing your policy during which you cannot claim maternity-related benefits—is a critical factor to consider. This period varies based on the insurer and the policy type.
Understanding Waiting Periods: Reasons and Types
Waiting periods in maternity insurance serve several purposes:
● Managing Risk: They mitigate the risk of individuals purchasing coverage only when pregnancy is imminent.
● Curbing Fraudulent Claims: They help discourage potential fraudulent claims.
Typical waiting periods for maternity insurance include:
● Initial Waiting Period (30-90 days): Applies to most health insurance plans.
● Maternity Benefit Waiting Period (9 months to 4+ years): Specific to maternity benefits.

Calculating Waiting Period Using LMP
To calculate the waiting period for maternity benefits using the Last Menstrual Period (LMP):
- Determine LMP: Identify the first day of your last menstrual period.
- Add 280 Days: Add 280 days (approximately 9 months and 7 days) to the LMP to estimate the due date.
- Example:
▪ If LMP is January 1, 2024:
○ Due Date = LMP + 280 days
○ Due Date = January 1, 2024 + 280 days
○ Due Date = October 8, 2024
This calculation helps estimate the due date, which is essential for planning when to purchase maternity insurance and understanding when you’ll be eligible for benefits.
GHI vs. RHI: The Waiting Period Difference
The key distinction between Group Health Insurance (GHI) and Retail Health Insurance (RHI) lies in their maternity benefit waiting periods:
● Group Health Insurance (GHI): Often provided by employers, GHI plans may feature shorter waiting periods for maternity coverage or even waive them entirely, making them advantageous for family planning.
● Retail Health Insurance (RHI): Individual RHI plans typically have longer waiting periods for maternity benefits compared to GHI plans.
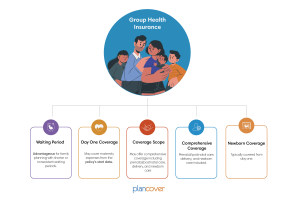
Maternity Coverage From Day One in GHI Plans
Group Health Insurance (GHI) plans, often provided by employers, may offer maternity benefits that start from day one of the policy. This means that the expecting mother is covered for maternity-related expenses as soon as the policy is in effect.
Day One Coverage: Available in some GHI plans, allowing immediate coverage for maternity-related hospitalization expenses.
Comprehensive Coverage: These plans may cover prenatal and postnatal consultations, delivery expenses, and newborn care from the very beginning.
Newborn Coverage: Newborns are typically covered from day one, providing significant protection for the infant’s health.
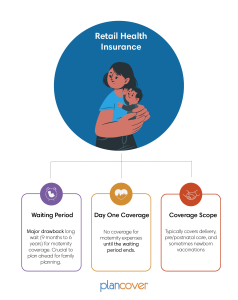
Waiting Period in RHI Plans
Retail Health Insurance (RHI) plans, on the other hand, usually come with a waiting period for maternity benefits. This waiting period can range from 9 months to 6 years, depending on the insurer and the specific policy.
Planning Ahead: It’s crucial for individuals to purchase RHI plans well in advance of planning a family due to the lengthy waiting periods.
Coverage Details: RHI plans typically cover delivery expenses, pre and postnatal care, and sometimes even newborn vaccinations after the waiting period is over.
Understanding the differences between GHI and RHI plans regarding maternity coverage is essential for informed decision-making when choosing the right insurance plan for your family planning needs.
Navigating Waiting Periods in India
To manage waiting periods for maternity insurance in India:
● Plan Early: Purchase maternity insurance well in advance of planning a family.
● Compare Plans Thoroughly: Scrutinize and compare waiting periods, coverage, and costs across different GHI and RHI plans.
● Prioritize GHI (if available): If your employer offers GHI, explore whether it offers more favorable maternity coverage terms and shorter waiting periods.
Understanding the concept of waiting periods and their differences between GHI and RHI plans is essential for informed decision-making about maternity insurance in India. Proactive planning, careful comparison across plans, and consulting with an insurance advisor will help you secure the most suitable and financially supportive coverage for your journey into parenthood.